Nutrigenomics is a rapidly growing area of research that holds great promise for advancing our knowledge about optimizing well-being and preventing illness. Remember that old saying, “you are what you eat?” There is some important truth to it. How our bodies interact with food plays a significant role in how well our cells function.
Nutrigenomics is a rapidly growing area of research that holds great promise for advancing our knowledge about optimizing well-being and preventing illness. Remember that old saying, “you are what you eat?” There is some important truth to it. How our bodies interact with food plays a significant role in how well our cells function.
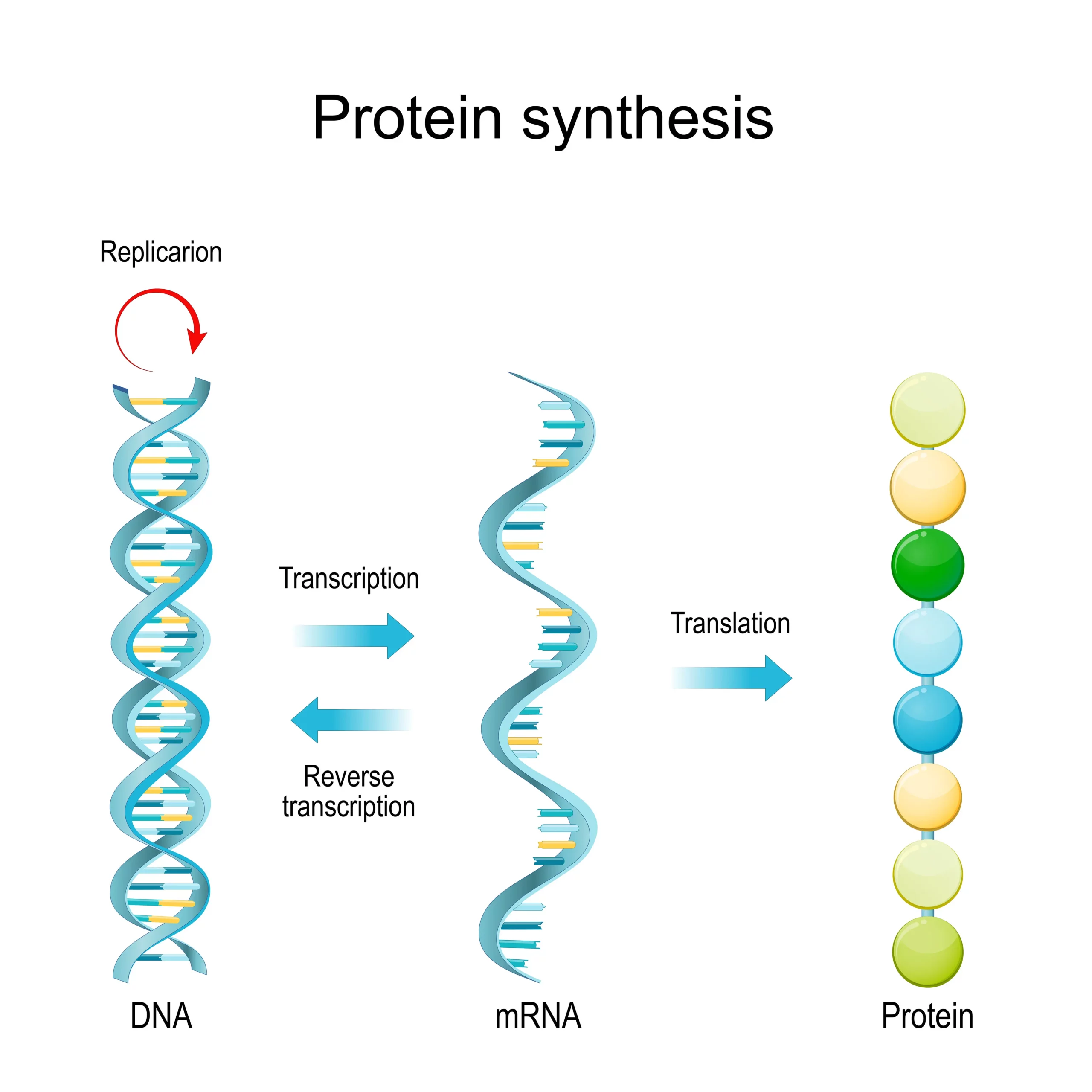
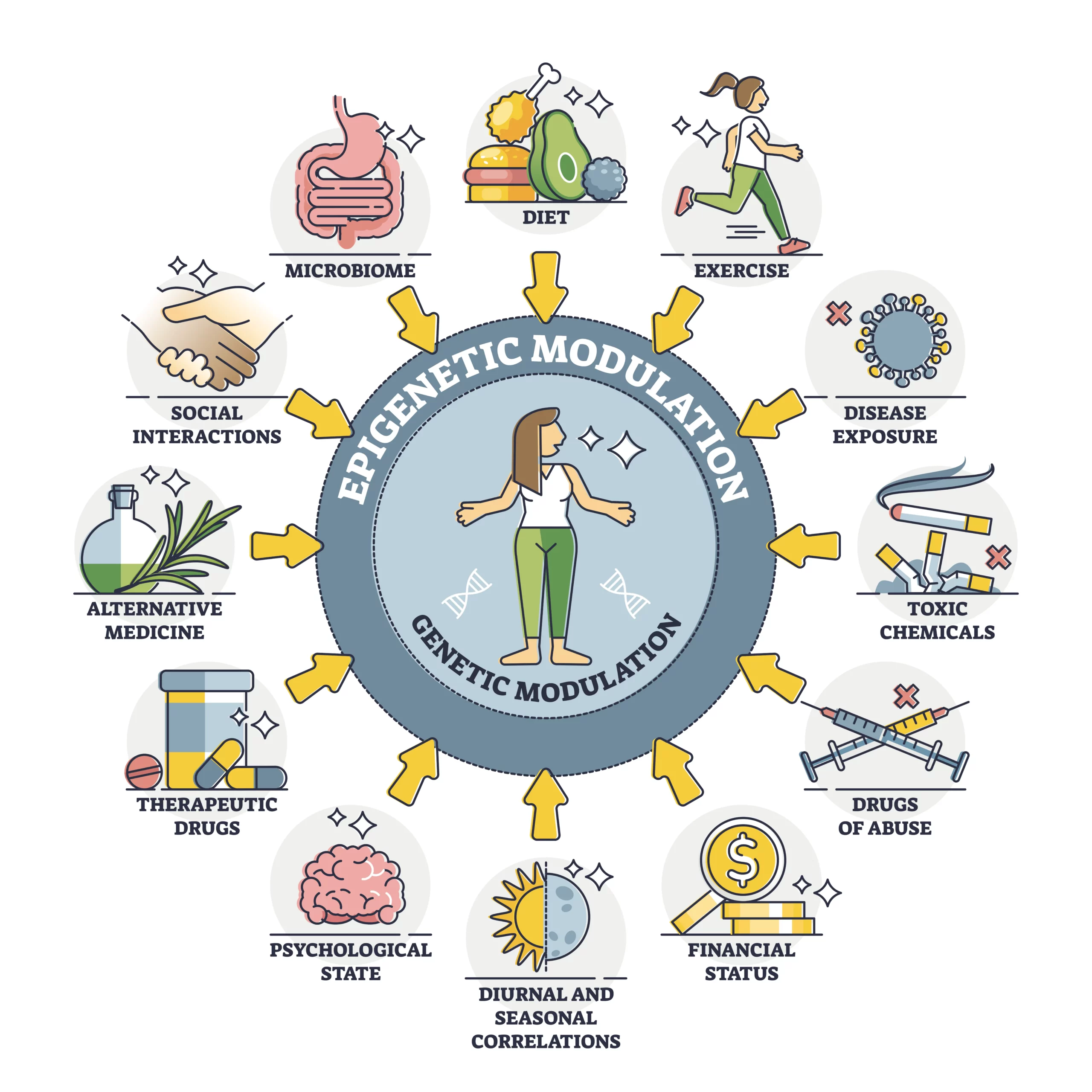
Nutrigenomics is the branch of science that studies how nutrition and genetics interact to influence our health and well-being. It examines how the nutrients in the foods we eat can affect gene function. But that’s just one side of the story. The relationship also goes in the opposite direction: our genetic makeup can affect our body’s response to different diets and nutrients.
This field of research brings together the disciplines of nutrition, genetics, and molecular biology to understand how thoughtful nutrition and supplementation can help prevent and manage health concerns.
Order your test now. You can order a single test or a family bundle (2 sets or 3 sets). Click below to order now.