Addressing inflammation is essential to improving overall wellness and reducing the risk of compounding health problems. Additionally, addressing chronic inflammation can enhance the effective management of other conditions, including methylation deficiencies, gut health, and overall body function. By addressing inflammation, individuals can take an active role in improving their health and well-being.
Inflammation isn’t just a physical issue; it can also affect our mental and emotional well-being. Chronic inflammation has been linked to an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health concerns, as well as feelings of exhaustion and difficulty concentrating.
The presence of body pain, arthralgia (joint pain), myalgia (muscle pain), chronic fatigue and insomnia, depression, anxiety and mood disorders, gastrointestinal complications, weight gain or weight loss, and frequent infections are all indications of chronic infection.
The good news is that we can fight back and improve our overall wellness in the process. From eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise to managing stress and incorporating supplements, there are many ways to reduce inflammation and improve our physical, mental, and emotional well-being.
It’s crucial to educate one’s self on the impact of chronic inflammation and the benefits of addressing it. Taking steps to reduce chronic inflammation improves health outcomes and enhances the ability to achieve wellness goals.
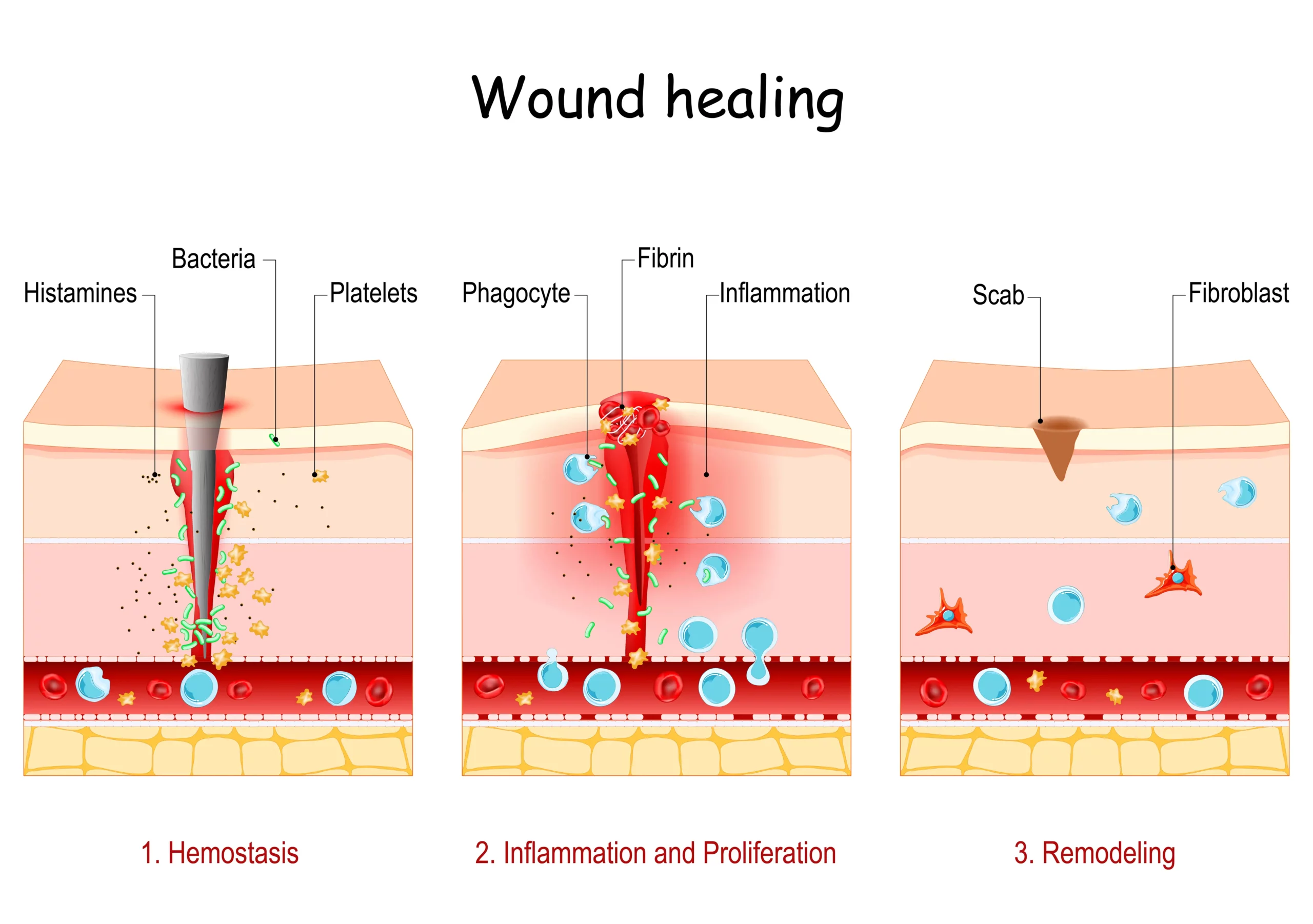
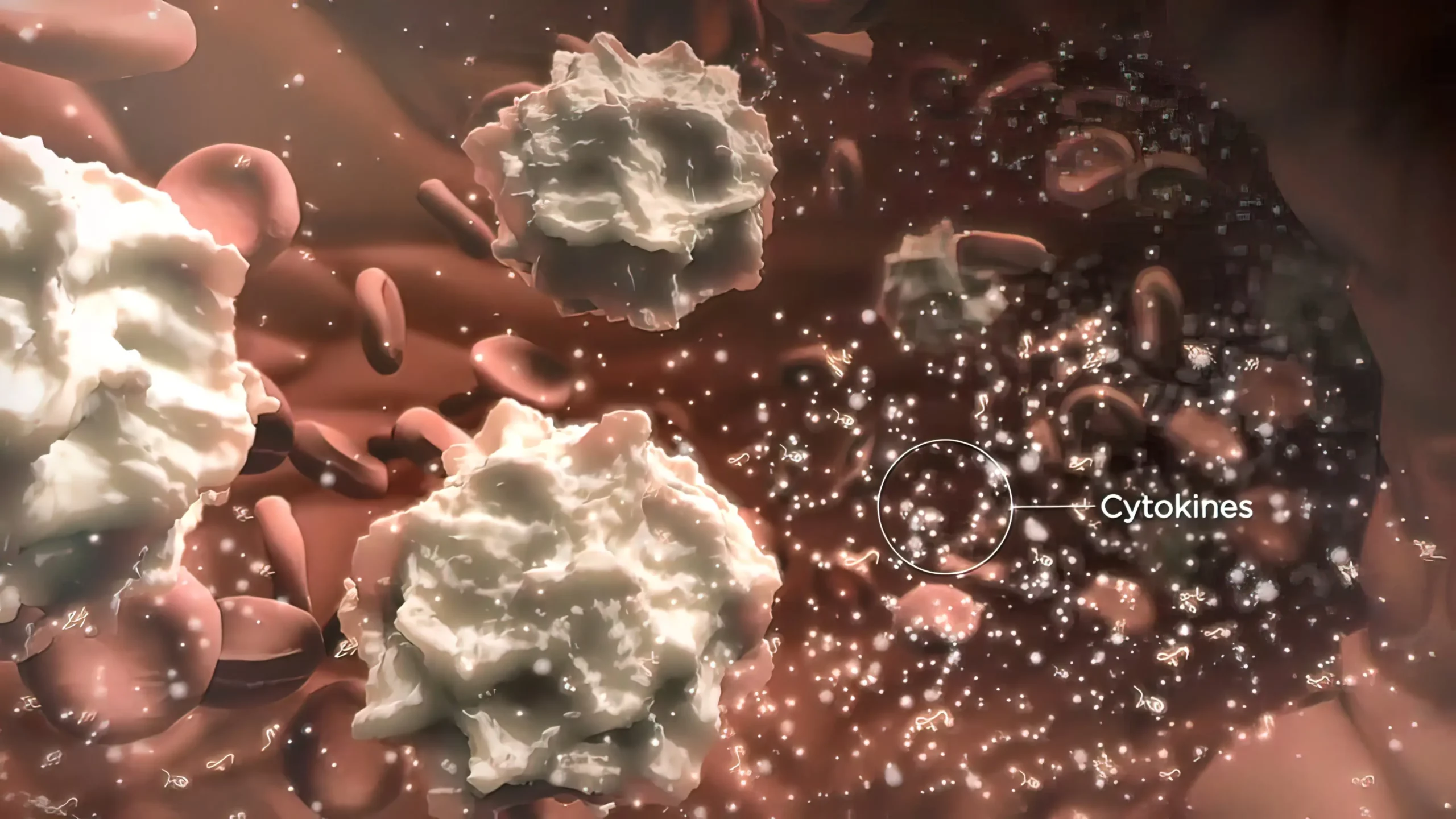
 Inflammation is a complex process that involves various immune cells, signaling molecules, and blood vessels. It is the body’s way of defending against foreign invaders, such as viruses and bacteria, and repairing damaged tissue. While acute inflammation is a routine and necessary response, chronic inflammation can lead to various health problems and negatively impact our physical, mental, and emotional well-being. In this lesson, we will explore the causes and consequences of chronic inflammation, how genetics plays a role in chronic inflammation, and discuss strategies for addressing this concern.
Inflammation is a complex process that involves various immune cells, signaling molecules, and blood vessels. It is the body’s way of defending against foreign invaders, such as viruses and bacteria, and repairing damaged tissue. While acute inflammation is a routine and necessary response, chronic inflammation can lead to various health problems and negatively impact our physical, mental, and emotional well-being. In this lesson, we will explore the causes and consequences of chronic inflammation, how genetics plays a role in chronic inflammation, and discuss strategies for addressing this concern.