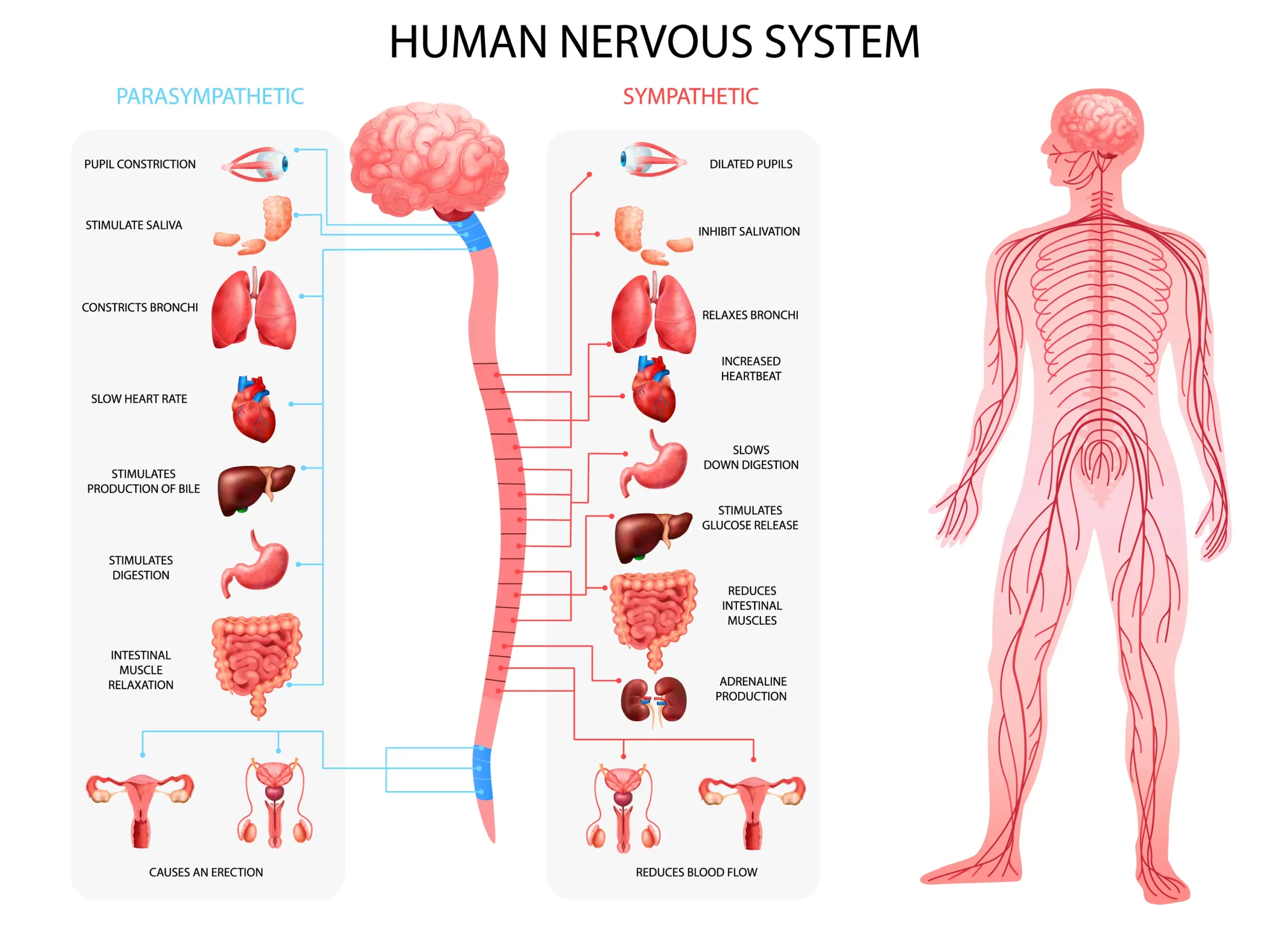
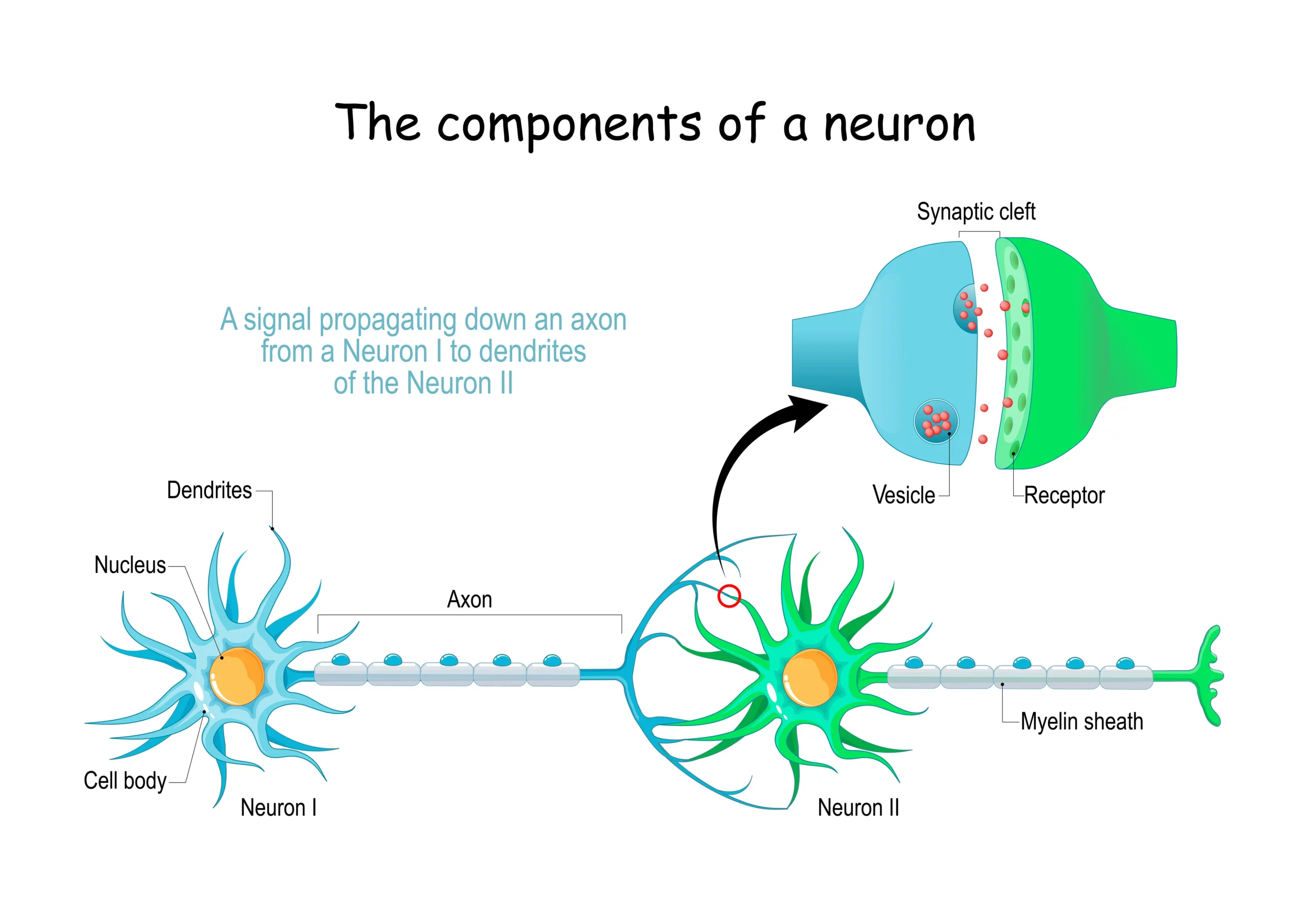
 The nervous system is the body’s communication network, consisting of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves that reach every part of the body. It plays a crucial role in coordinating and integrating the body’s functions, receiving and processing sensory information, and initiating actions in response to stimuli. The brain is often referred to as the control center of the nervous system and is responsible for processing and integrating information from the senses, controlling movement and coordination, and regulating bodily functions such as heart rate and blood pressure.
The nervous system is the body’s communication network, consisting of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves that reach every part of the body. It plays a crucial role in coordinating and integrating the body’s functions, receiving and processing sensory information, and initiating actions in response to stimuli. The brain is often referred to as the control center of the nervous system and is responsible for processing and integrating information from the senses, controlling movement and coordination, and regulating bodily functions such as heart rate and blood pressure.
Order your test now. You can order a single test or a family bundle (2 sets or 3 sets). Click below to order now.